Inner Sphere Trees for 6-DOF Haptic Rendering
Inner Sphere Trees ( ) are a novel geometric data structure for approximate collision detection at haptic rates. They support different kinds of queries, namely, proximity queries
and a new method for interpenetration computation, the penetration
volume in one unified algorithm. In addition, the application does not need to know in advance which situation exists between the pair of objects. ) are a novel geometric data structure for approximate collision detection at haptic rates. They support different kinds of queries, namely, proximity queries
and a new method for interpenetration computation, the penetration
volume in one unified algorithm. In addition, the application does not need to know in advance which situation exists between the pair of objects.
The penetration volume is related to the amount of water being displaced by the overlapping region and, thus, corresponds to a physically motivated force. It allows us to define a novel penalty-based collision response
scheme that provides continuous forces and torques which
are applicable to physically-based simulations as well as to haptic
rendering scenarios.
The main idea is to bound objects from the inside with a
set of non-overlapping spheres. Based on such sphere packings,
we construct an
"inner bounding volume hierarchy"
by extendeding an AI clustering algorithm.
The results show performance at haptic rates both for proximity
and penetration volume queries for models consisting of
hundreds of thousands of polygons.
Sphere Packing
In our current implementation of the inner sphere trees, we use a simple heuristic to fill the objects densly with spheres.
It is based on discrete distance fields in combination with a greedy sphere creation algorithm that offers a good trade-off between
accuracy and speed in practice.
Building the IST
Based on the sphere packing, we create a bounding volume hierarchy.
To do so, we use a recursive top-down wrapped hierarchy approach. The partitioning of the spheres is based on a clustering
algorithm called batch neural gas with magnification control (i.e., larger
spheres get larger weights).
In the above two screenshots, you can see two levels of the hierarchy (left =
first level, right = second level); spheres of the same color belong to the
same cluster and, thus, to the same sub-tree.
Contact Forces
Forces and torques are computed for every pair of overlapping spheres
individually. This results in continuous penalty forces and torques, provided
the paths of the objects is continuous. This is essential for stable physically-based simulations and haptic rendering.
Download
The ISTs will be integrated into the CollDet-Library in the near future.
Until then, you can
send us an email
, and maybe we can send you an intermediate version.
Publications
- Inner Sphere Trees for Proximity and Penetration Queries, Robotics Science and Systems (RSS), June 29 - July 2, 2009. [BibTex]
- A Unified Approach for Physically-Based Simulations and Haptic Rendering, ACM SIGGRAPH Video Game Proceedings,
New Orleans, USA, August 2009. [BibTex]
-
Stable 6-DOF Haptic Rendering with Inner Sphere Trees, Proceedings of International Design Engineering Technical Conferences & Computers and Information in Engineering Conference (IDETC/CIE),
San Diego, USA, 30 August - 02 September 2009. [BibTex]
Videos
Click on the pictures to watch the videos.
Overview
 |
| This video gives an overview over the ISTs (no audio) |
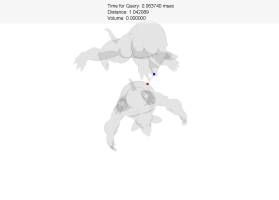
Proximity Queries
 |
 |
| Two armadillos |
Two cows |
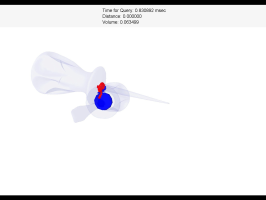
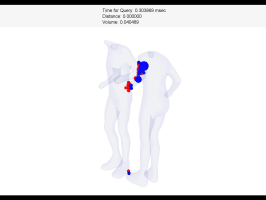
Penetration Volume
 |
 |
 |
| Dragons |
Screw drivers |
Two torsos |
ISTs in Haptic Environments
 |
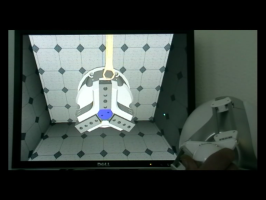 |
| Multibody simulation with haptic support |
Another haptic scene |
This work was partially supported by DFG grant ZA292/1-1 and the
 research project, founded by the Federal Minstry of Education and Research (BMBF) grant Avilus / 01 IM 08 001 U. research project, founded by the Federal Minstry of Education and Research (BMBF) grant Avilus / 01 IM 08 001 U.
|